The Monday, April 8, 2024, total solar eclipse will cross North America, passing over Mexico, the United States, and Canada. The total solar eclipse will begin over the South Pacific Ocean. Weather permitting, the first location in continental North America that will experience totality is Mexico’s Pacific coast at around 11:07 a.m. PDT.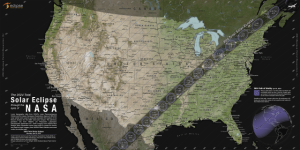
The path of the eclipse continues from Mexico, entering the United States in Texas, and traveling through Oklahoma, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, Kentucky, Indiana, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine. Small parts of Tennessee and Michigan will also experience the total solar eclipse. The eclipse will enter Canada in Southern Ontario, and continue through Quebec, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Cape Breton. The eclipse will exit continental North America on the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada, at 5:16 p.m. NDT.
New map calculations have raised some concerns that the path of totality — where it’s possible to see the moon completely block out the sun — is slightly narrower than NASA calculated. That means some cities on the edge of the route that were expecting to experience a second or two of total darkness might be left out.
NASA has not changed its predictions, but the space agency advises that there is some uncertainty involved in mapping the eclipse’s path.
“Calculations that use a slightly larger radius for the size of the Sun yield an eclipse path that is slightly narrower,” said NASA spokesperson Karen Fox in an emailed statement. “This difference would only affect cities on the very edge of the path of totality, where blanket predictions are difficult regardless — a few city blocks one way or the other could mean 20, 10, or 0 seconds of totality.”
A solar eclipse occurs during the new moon phase, when the moon passes between Earth and the sun, casting a shadow on Earth and totally or partially blocking our view of the sun. While an average of two solar eclipses happen every year, a particular spot on Earth is only in the path of totality every 375 years on average, Astronomy reported
Related posts
Categories
- Advertisements (1)
- Agriculture (46)
- Breaking News (26)
- Business (599)
- Crime (994)
- Education (322)
- Entertainment (128)
- Features (13)
- For The Records (43)
- Foreign News (1,203)
- Health (220)
- Home News (332)
- Interview (9)
- Judiciary (355)
- Lifestyle (140)
- Local News (112)
- National News (1,449)
- Opinion (26)
- Politics (1,020)
- Religion (158)
- Science and Technology (125)
- Security (688)
- Sports (883)
- States' News (824)
- Transportation (331)
- Uncategorized (10)

